An insurance policy is a legally binding contract between an individual (the policyholder) and an insurance company. In this agreement, the insurer commits to providing financial protection or reimbursement to the policyholder for specific losses, damages, or liabilities, as outlined in the terms and conditions of the policy. In exchange, the policyholder agrees to pay a specified premium to maintain coverage. Understanding the fundamentals of insurance policies, their types, components, and the way they operate is crucial for making informed decisions about financial protection.
Types of Insurance Policies
Insurance policies come in various forms to address different aspects of life, health, property, and liabilities. The following are some of the most common types of insurance policies:
1. Life Insurance
Life insurance provides a financial benefit to the beneficiaries of the insured in the event of the policyholder’s death. It is designed to ensure that loved ones are taken care of financially, covering expenses such as mortgage payments, college tuition, and other living expenses. There are two primary types of life insurance policies:
- Term Life Insurance: This policy provides coverage for a specified term, such as 10, 20, or 30 years. If the policyholder dies within the term, the beneficiaries receive the death benefit.
- Permanent Life Insurance: Unlike term life insurance, permanent life insurance offers lifetime coverage and includes a cash value component that grows over time.
2. Health Insurance
Health insurance helps cover the cost of medical expenses, including doctor visits, hospital stays, prescription medications, and preventive care. Policyholders may pay premiums, co-payments, and deductibles, but the insurance reduces the financial burden of unexpected healthcare costs.
3. Auto Insurance
Auto insurance protects policyholders against financial losses related to vehicle damage, accidents, theft, and liability. There are different types of auto insurance coverage:
- Liability Coverage: Covers damage or injuries caused to others in an accident.
- Collision Coverage: Pays for damages to the policyholder’s vehicle due to a collision.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Covers non-collision-related incidents, such as theft, vandalism, or natural disasters.
4. Homeowners and Renters Insurance
- Homeowners Insurance: Provides coverage for damages to the structure of a home, personal belongings, and liability in case of accidents occurring on the property.
- Renters Insurance: Offers coverage for personal property inside a rented dwelling, along with liability protection.
5. Disability Insurance
Disability insurance replaces a portion of the policyholder’s income if they become unable to work due to illness or injury. There are short-term and long-term disability policies available, each catering to different durations of coverage.
6. Travel Insurance
Travel insurance covers expenses related to trip cancellations, medical emergencies, lost baggage, and other travel-related incidents. This type of insurance is particularly useful for international travelers who may face unforeseen events.
How Does an Insurance Policy Work?
An insurance policy functions based on a simple risk management concept: the policyholder pays a premium, and in return, the insurer provides a financial safeguard against specific risks. Here’s how the key elements of an insurance policy work:
1. Premiums
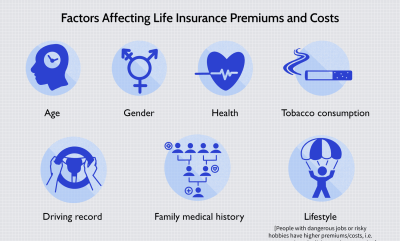
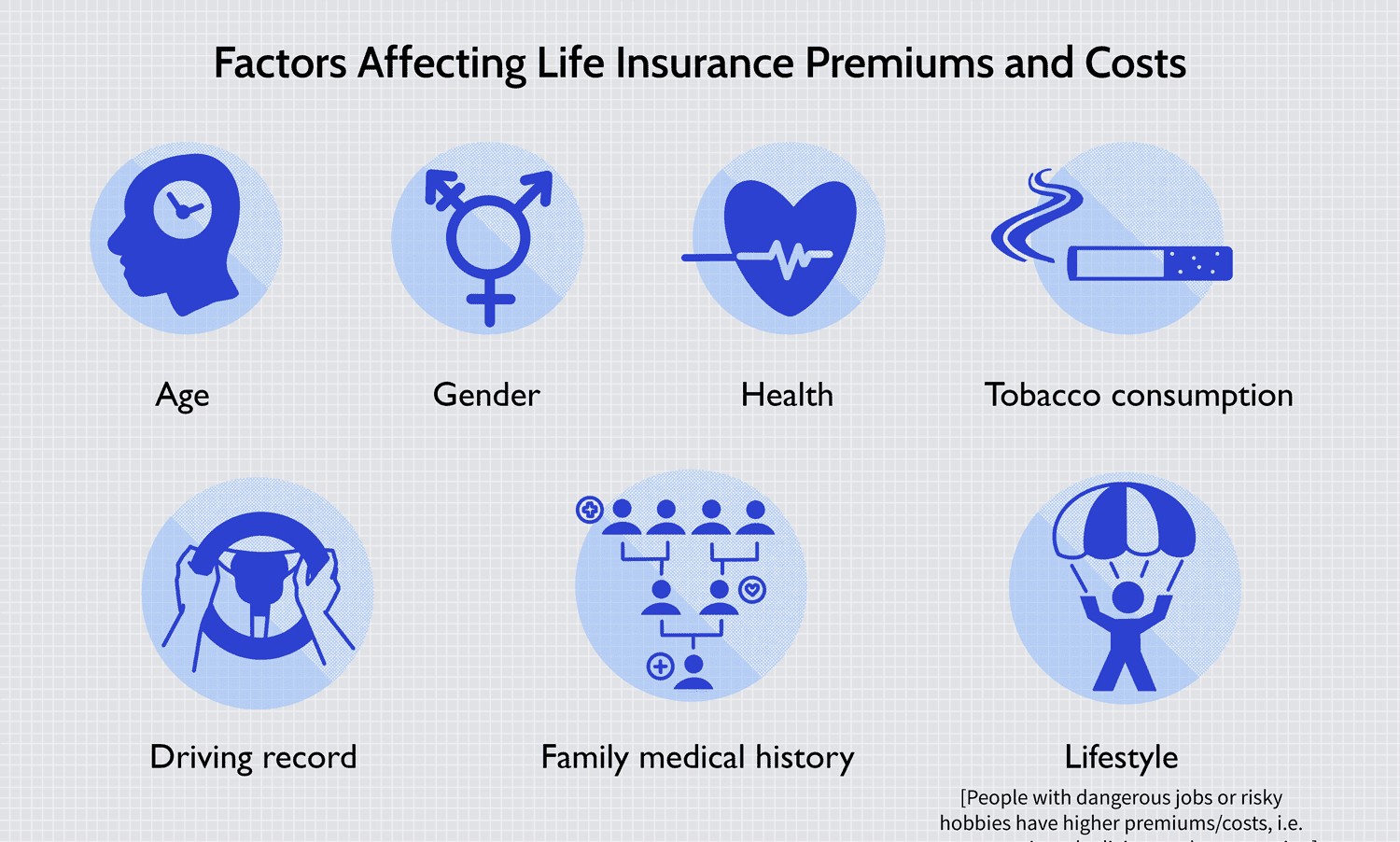
The premium is the amount the policyholder pays periodically (monthly, quarterly, or annually) to keep the insurance coverage active. The premium amount is determined by factors such as the type of insurance, coverage amount, the policyholder’s age, health status, lifestyle, and any potential risk factors associated with the insured asset or individual.
2. Deductibles
A deductible is the amount the policyholder must pay out-of-pocket before the insurance company starts covering a claim. For instance, if a health insurance policy has a $1,000 deductible, the policyholder must pay the first $1,000 of medical expenses before the insurer contributes.
3. Coverage Limits
Coverage limits define the maximum amount an insurance company will pay for a covered claim. For example, an auto insurance policy may have a $50,000 limit for bodily injury coverage, meaning the insurer will only pay up to that amount for claims related to bodily injuries.
4. Policy Exclusions
Insurance policies often include exclusions—specific conditions or circumstances that are not covered. For example, homeowners insurance may exclude damage from floods, requiring separate flood insurance for such coverage.
5. Claims Process
When a policyholder experiences a loss or an incident covered by their insurance policy, they file a claim with the insurer. The insurance company evaluates the claim, assesses the damage or loss, and determines the amount of compensation based on the policy terms. If the claim is approved, the insurer pays out the claim amount, less any applicable deductible.
The Importance of Insurance Policies
Insurance policies play a vital role in providing financial security and peace of mind. They help individuals and businesses manage risks and recover from losses that would otherwise be financially devastating. Here are some key benefits of having insurance coverage:
1. Protection Against Financial Loss
Insurance acts as a safety net that reduces the financial impact of unforeseen events such as accidents, natural disasters, theft, illness, or death. By covering these risks, insurance prevents individuals and families from having to bear the full cost of significant losses.
2. Compliance with Legal Requirements
Some types of insurance are legally required. For example, auto insurance is mandatory in most states to operate a vehicle, and health insurance may be required under certain regulations. Meeting these requirements protects against potential legal penalties and financial liabilities.
3. Investment and Savings Opportunities
Certain insurance policies, such as permanent life insurance, offer a cash value component that grows over time and can be used as a savings or investment vehicle. Policyholders can borrow against the cash value or use it to pay premiums.
4. Risk Management for Businesses
Businesses use insurance to manage operational risks, protect assets, and ensure continuity in case of losses. Policies like commercial property insurance, liability insurance, and workers’ compensation insurance are crucial for businesses to shield themselves from significant financial disruptions.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Insurance Policy
Selecting the right insurance policy requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure adequate protection and value for money:
1. Assessing Coverage Needs
Evaluate the level of coverage needed based on individual circumstances, such as health conditions, family dependents, property value, and lifestyle. Overestimating or underestimating coverage can lead to financial strain in the event of a claim.
2. Comparing Premiums and Deductibles
While lower premiums may be attractive, they often come with higher deductibles and less coverage. It is important to balance affordability with adequate protection to avoid unexpected out-of-pocket expenses.
3. Reviewing Policy Exclusions and Limitations
Carefully review the policy terms to understand what is excluded. This ensures that the policyholder is aware of any gaps in coverage and can seek additional policies if necessary.
4. Checking the Insurer’s Reputation
Choose an insurance company with a strong reputation for customer service, financial stability, and fair claims processing. Reading reviews and checking ratings can help determine if an insurer is reliable.
Common Insurance Terms You Should Know
Understanding insurance jargon is essential for selecting the right coverage. Here are some common terms:
- Beneficiary: The person or entity designated to receive benefits from an insurance policy.
- Endorsement: A written amendment to the insurance policy that modifies coverage.
- Grace Period: A specified time after the premium due date during which coverage remains in effect without penalty.
- Rider: An additional provision added to an insurance policy that provides extra benefits or coverage.
Conclusion
Insurance policies are essential tools for protecting against unexpected financial losses. Understanding the various types, how they work, and what factors to consider when choosing a policy can significantly enhance financial planning. Whether it’s life, health, auto, or homeowners insurance, having the right coverage provides peace of mind and financial security.